11 August 2016 Today’s Throwback Thursday article, first published a month ago and now free, shows just how much progress is being made today in unearthing the role of microbes in regionally distinct wine flavours – progress that should encourage our microbiologist heroes around the world. See also Max Allen’s recent report on first steps in terroir studies in Australia.
6 July 2016 Do microbes, fungi and wine metabolites set your heart racing? Not yet, maybe, but they are starting to help to answer some of our many questions about the hidden nature of terroir and why some wines taste the way they do, why a vine grown in a specific place produces a wine that could come from nowhere else. It is no longer enough to analyse soil and climate, we now have to investigate on a much smaller scale.
One of the 300 new entries in the latest, fourth edition of the Oxford Companion to Wine – microbial terroir – touches on this theme and draws on the work of several academics whose hearts are racing, including Professor David Mills at UC Davis and his former student Dr Nick Bokulich, recently moved to Northern Arizona University.
They and their co-authors, Thomas S. Collins, Chad Masarweh, Greg Allen, Hildegarde Heymann, Susan E. Ebeler, last month published ‘Associations among wine grape microbiome, metabolome, and fermentation behavior suggest microbial contribution to regional wine characteristics’ in mBio, the open-access online journal published by the American Society for Microbiology. (See http://mbio.asm.org/content/7/3/e00631-16.long for the full text.)
The opening sentence of their abstract perfectly sums up the current state of knowledge in terms of our ability to explain the intermediary role of bacteria and fungi in connecting soil and climate to how wines taste: ‘Regionally distinct wine characteristics (terroir) are an important aspect of wine production and consumer appreciation. Microbial activity is an integral part of wine production, and grape and wine microbiota present regionally defined patterns associated with vineyard and climatic conditions, but the degree to which these microbial patterns associate with the chemical composition of wine is unclear.’
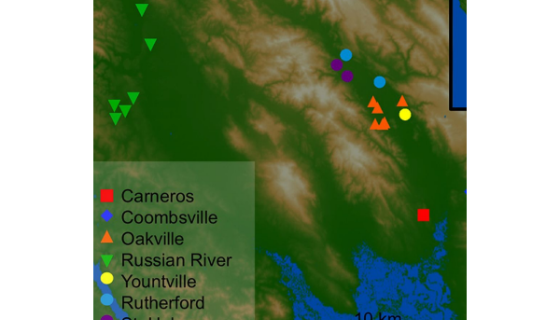
Their study of 200 commercial wine fermentations showed that ‘The bacterial and fungal consortia of wine fermentations, composed from vineyard and winery sources, correlate with the chemical composition of the finished wines’ and that ‘grape and wine microbiota [the micro-organisms of a particular site] exhibit regional patterns that correlate with wine chemical composition, suggesting that the grape microbiome [the combined genetic material of a particular site] may influence terroir’. (The image above is taken from figure 1 in the Mills et al paper cited in full above, showing the sources of the grapes for the ferments that were studied; courtesy of the Creative Commons international licence.)
It is notable that the authors emphasise early in their paper that this research has commerical implications: ‘In addition to enriching our understanding of how growing region and wine properties interact, this may provide further economic incentives for agricultural and enological practices that maintain regional microbial biodiversity’. In other words, look after your microbes and the regional distinctiveness of your wine may bring financial rewards.
Having recognised the role of terroir in its traditional definition in ‘increasing the consumer demand for and economic value of many regional products’, distinguishable analytically as well as organoleptically and protected by law (PDOs and AVAs, for example), they set out to determine how microbial biogeography – the localisation of specific microbes to specific places – contributes to regional wine characteristics.
In their earlier work on microbial biogeography, Bokulich and Mills and their co-authors had shown that region, grape variety and climate ‘shape the bacterial and fungal communities of wine grapes across multiple growing years’ (Bokulich NA, Thorngate JH, Richardson PM, Mills DA, ‘Microbial biogeography of wine grapes is conditioned by cultivar, vintage, and climate’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 111 (2014): E139–E148.). This complements work in New Zealand by Mat Goddard and his colleagues that showed just how region-specific – even winery-specific – yeasts can be.
While yeasts are a critical part of microbial terroir, at least for wines which are fermented without the use of inoculated commercial yeast strains, they are not the only microbes that influence the expression of terroir in wine composition and flavour.
The authors’ experiments on 200 musts, fermentations and finished wines of Cabernet Sauvignon and Chardonnay grapes grown in individual vineyards in Napa and Sonoma used high-throughput marker-gene sequencing and ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography/quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry to identify bacteria and fungi and to look for correlations and patterns of distribution between the microbiota of a particular vineyard and the metabolome (all the substances formed in or necessary for metabolism) of the wine made from it, and then for associations between the microbiome, the composition of the must prior to fermenation and the progress of fermentation. All the samples were taken from Far Niente and Nickel & Nickel wineries in Oakville, Napa.
They found that there were regional distinctions between grape/wine microbiota and that these microbiota did indeed correlate with wine composition and fermentation performance, and also that the microbial composition of the must predicts the composition of the finished wine. Interestingly, and perhaps unexpectedly, ‘Chardonnay demonstrated stronger AVA differentiation for both bacterial and fungal profiles than Cabernet Sauvignon’. Regional difference decreased during fermentation, particularly in the reds that went through malolactic fermentation and were thus influenced by the presence and activity of lactic acid bacteria.
They underline that the ability to predict the metabolites in the wine from the microbial composition of the must is not the same as claiming causation. But the results do seem to suggest that the correlations should form part of our understanding of, and ability to quantify, terroir.
In their conclusion they make modest but significant claims: ‘The intricacies of wine flavor are not determined by microbial composition alone. We conjecture that microbial activity contributes to the mixture of abiotic and biotic factors that underlie wine terroir, with the scale of this contribution depending upon the winemaking techniques and style of wine produced.’ However, returning to their early reference to commercial significance, they suggest that the microbial constituents of grape musts could provide information to winemakers to allow them to improve their wines (or, perhaps equally important, avoid problem fermentations).
When I asked Professor Tom Gilbert of the Natural History Museum of Denmark and one of the project architects behind MicroWine what he thought of this work, he replied, ‘I’d heard of this study from David Mills in person … Ultimately I think it’s visionary – it’s exactly the kind of thing we are aiming at [with MicroWine]. Only when we better understand the exact roles of local microbes in wine flavour, and what exactly affects which microbes can grow where, will we be able to really begin to understand what drives local flavour variation.’
Also due for publication later this year in Food Research International (and online) is ‘Perceived minerality in sauvignon blanc wine: chemical reality or cultural construct?’, the final part of research by Wendy V Parr, Dominique Valentin, Jason Breitmeyer, Dominique Peyron, Philippe Darriet, Robert Sherlock, Brett Robinson, Claire Grose and Jordi Ballester which ‘aimed to determine the relationship between perceived mineral character in wine and wine chemical composition’. This is a further example of the way experimental techniques are allowing us to identify the connections we have been missing and to improve the way we talk about wine.